STD Symptoms
Information About Our Chlamydia Testing Service
We utilize the FDA-cleared Nucleic Acid Amplification (NAA) test, which is recognized as the most precise Chlamydia testing method available. Our Chlamydia test involves a simple urine sample, providing results in just 1-2 days. This test is swift and hassle-free, with no fasting, swabbing, pricking, or undressing required. We pride ourselves on the accuracy of our lab tests, with the Chlamydia test boasting an impressive 99.3% specificity and 99.8% sensitivity.
Select Your Testing Packages
- Chlamydia Test – $59.00
- Chlamydia & Gonorrhea Test – $99.00
- 10 Test Panel – $139.00
- 10 Test Panel with HIV RNA Early Detection – $259.00
Chlamydia Testing Procedure
- No Urinating
Refrain from urinating for at least one hour before your testing center visit.
- 5-Minute Testing Procedure
- Sample Needed
Small Urine Specimen
- Quick Results
Available within 1-2 Days
- Physician Consultation Conducted via phone for positive results
Additional Details Regarding Our Chlamydia Urine Test
Which specimen is used for Chlamydia testing: blood or urine?
Urine-Based Chlamydia Testing
Our Chlamydia test involves the collection of a urine sample at the lab. There’s no need for a blood sample in Chlamydia testing. This NAA Chlamydia test is hassle-free and doesn’t involve pricking, swabbing, or undressing.
Preparing for a Chlamydia Urine Test: To prepare for your Chlamydia urine test, remember the following:
- Urination: Refrain from urinating for at least one hour before the test.
- First-Catch Urine: The sample should be the first 20-30mL of your initial urine stream, known as first-catch urine.
- Sample Purity: Ensure the sample only contains first-catch urine to avoid dilution.
- Female Test Takers: Females are advised not to cleanse the labial area before providing the sample.
- No Fasting: Fasting is not required.
- No Additional Preparation: There is no need for any other special preparation
When to Get Tested for Chlamydia: If you suspect recent exposure to chlamydia, our medical experts recommend the following testing timelines:
- 1-5 Days Post-Exposure: Wait at least 1-5 days after a potential chlamydia exposure for testing.
- Minimum 24 Hours: At the very least, allow 24 hours to pass after suspected chlamydia exposure.
- Optimal Timing: For the most precise results, consider testing two weeks after potential exposure.
- Post-Treatment Testing: If you’ve undergone chlamydia treatment, get retested 21 to 28 days after treatment completion to confirm eradication of the bacterium.
- Gonorrhea and Chlamydia: If you test positive for gonorrhea, it’s advisable to also get tested for chlamydia, as these infections often co-occur, and their symptoms are very alike.
Understanding Your Chlamydia Test Results:
Interpreting the results of your chlamydia test is straightforward:
- Positive Results: A positive result indicates the presence of the Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria in your system, confirming a chlamydia infection.
- Negative Results: A negative result means you do not have chlamydia.
However, it’s essential to consider the timing of your test:
- Timing Matters: If you test too soon after potential exposure, your results may not be entirely accurate.
For the most reliable results, it’s advisable to wait for up to two weeks post-potential exposure.
Is Chlamydia Treatable?
Yes, Chlamydia is completely treatable with antibiotics. If you receive a positive test result, you can have a remote consultation with one of our doctors to discuss treatment options. If necessary, antibiotics can be prescribed and obtained from your nearby pharmacy.
Who Should Get Tested for Chlamydia?
Chlamydia is a concern for both women and men. The CDC reports nearly 3 million new chlamydia cases annually in the U.S. It’s highly prevalent because it often presents no symptoms and spreads easily. According to the CDC, “chlamydia prevalence among sexually active individuals aged 14-24 years is nearly three times the prevalence among those aged 25-39 years.”
The CDC strongly recommends chlamydia testing for all sexually active women aged 25 or younger. Chlamydia is more common among young women because their cervix is still developing, making it more susceptible to infection. However, regardless of age, if you’ve recently had unprotected intercourse with a partner of unknown STD status, getting tested for chlamydia is advisable.
When is the Best Time to Get Tested for Chlamydia?
Being aware of your sexual health is crucial. The ideal time to consider chlamydia testing is now. If you suspect recent exposure to chlamydia, it’s advisable to wait a few days before getting tested. Waiting at least 1-5 days after potential exposure is recommended, with two weeks being the most reliable timeframe.
After completing chlamydia treatment, it’s vital to get retested at 21 to 28 days to confirm the bacterium’s elimination from your system.
For those who have tested positive for gonorrhea, immediate chlamydia testing is crucial. Chlamydia and gonorrhea often occur together, and having one infection makes you more susceptible to the other. To simplify the process, we offer the chlamydia/gonorrhea test panel.
If you are unsure of your sexual health status regarding any of the common STDs, including gonorrhea, syphilis, HIV-1, HIV-2, Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, HSV-1, or HSV-2, our doctors highly recommend the 10 Test Panel, covering all 10 of the most prevalent STDs.
We utilize the FDA-cleared Nucleic Acid Amplification (NAA) test, which is recognized as the most precise Chlamydia testing method available. Our Chlamydia test involves a simple urine sample, providing results in just 1-2 days. This test is swift and hassle-free, with no fasting, swabbing, pricking, or undressing required. We pride ourselves on the accuracy of our lab tests, with the Chlamydia test boasting an impressive 99.3% specificity and 99.8% sensitivity.
“Gonorrhoea, often referred to as “the drip” or “the clap,” is a prevalent bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It spreads through sexual contact and affects the reproductive systems of both men and women, including the cervix, fallopian tubes, uterus, and urethra. Gonorrhoea can also infect the throat and anus through oral or anal sex. Immediate treatment with antibiotics is crucial because untreated gonorrhoea can lead to severe health complications, including infertility. Regular STI testing is essential, even if you don’t experience symptoms, to effectively detect and manage this STI.
Symptoms of Gonorrhoea:
Gonorrhoea often remains asymptomatic in many men and most women. In men, it can cause:
- Painful urination
- Penile discharge
- Swollen testicles
In women, symptoms may include:
- Pain or burning during urination
- Increased vaginal discharge
- Vaginal bleeding between periods
Gonorrhoea can also infect the rectum, leading to various discomforts.
Gonorrhoea Beyond the Genitals:
Gonorrhoea can extend beyond the genital area:
- Joint Impact: It can cause painful joint inflammation, potentially resulting in long-term damage and arthritis.
- Rectal Trouble: Rectal gonorrhoea can result from anal sex with an infected partner, potentially causing pain, discharge, and bleeding.
- Eye Infections: In newborns, gonorrhoea can lead to eye infections and blindness if transmitted during childbirth.
How Gonorrhea Spreads:
Gonorrhoea spreads through sexual contact and can also be transmitted from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth.
At-Risk Groups:
Although anyone sexually active can contract gonorrhea, certain groups face a higher risk due to their behavior and biology. Regular testing is recommended for specific groups.
Gonorrhoea Prevalence:
Gonorrhoea is a widespread global health concern, affecting millions of people each year. In the United States, it ranks as a common bacterial STI, although many cases go undiagnosed due to the absence of symptoms.
Preventing Gonorrhoea:
While abstinence is the most foolproof prevention method, consistently using condoms and practicing mutual monogamy with testing can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Meet the Culprit - Gonococcus:
Gonococcus, scientifically known as Neisseria gonorrhoeae, is the bacterium responsible for gonorrhoea. Its name is derived from its appearance under a microscope, and it was coined by a German physician and bacteriologist in 1879. While “gonococcus” is a medical term, many are more familiar with the condition itself.”
Hepatitis A Antibody Blood Test Process
Our laboratory conducts an FDA-approved blood test for hepatitis A, specifically targeting the Hepatitis A Virus (HAV) in your bloodstream. This test checks for IgM antibodies, proteins generated by your body as a response to a viral infection. The presence of these antibodies indicates exposure to the hepatitis A virus. Our FDA-certified hepatitis A test boasts exceptional accuracy, with sensitivity and specificity rates both reaching an impressive 95 percent.
The Process of Hepatitis A Testing
5-Minute Testing Procedure
Small Blood Sample Required
Results Available in 1-2 Days
Phone Consultation with Doctor for Positive Results
Additional Details on Hepatitis A Testing
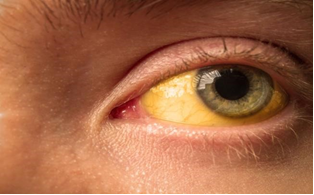
Hepatitis A Testing Procedure
Our hepatitis A test is conducted using a blood sample, which is known for its superior accuracy compared to urine or alternative testing methods for hepatitis A. When you come to our testing center, a lab technician will skillfully collect a small blood sample.
Preparation for the Test
No special preparation is needed before your visit to the testing center. Fasting is not necessary.
How Did I Get Hepatitis A?
Hepatitis A typically spreads when an individual consumes the virus through contaminated food or beverages that have traces of stool from an infected person, even if not visible. Additionally, if you’ve recently traveled to a developing country, your risk of contracting hepatitis A is higher. This virus can also be transmitted through sexual contact.
Highest Risk Groups for Hepatitis A
Individuals who have visited developing countries with a significant hepatitis A prevalence, engaged in anal or potentially infected sexual activity, or used shared needles for illicit drug use are at the greatest risk of contracting hepatitis A and should consider testing. For the most accurate results, it’s recommended to wait 2-7 weeks after potential exposure before undergoing a hepatitis A test.
Require Assistance Interpreting Your Test Results?
Your hepatitis A test outcome will be categorized as either positive or negative. A positive outcome signifies an acute or recent HAV infection, while a negative outcome indicates the absence of an active hepatitis A infection.
Can Hepatitis A Be Managed or Prevented?
Hepatitis A currently has no cure, but a highly safe and effective vaccine is available to protect against the virus. The hepatitis A vaccine has been in use since the 1990s, significantly reducing hepatitis A cases. If you haven’t been vaccinated before, it’s possible to receive the vaccine within two weeks of virus exposure, offering an 80-90% likelihood of avoiding symptoms.
Who Should Consider Hepatitis A Testing?
Individuals who have never had Hepatitis A or haven’t received the Hepatitis A vaccine are at risk of contracting the virus. Hepatitis A can be commonly transmitted through improperly prepared food, sexual activity, and needle sharing. Those at an elevated risk of Hepatitis A include travelers to developing countries, men who have sex with men, and individuals in close contact with individuals infected with hepatitis A.
When to Get Tested for Hepatitis A
The ideal time for hepatitis A testing is now. Take charge of your sexual health today. To achieve the most accurate results, it’s advisable to wait until after the incubation period, the time between exposure to the virus and the onset of symptoms. In the case of hepatitis A, it’s best to wait at least 14-35 days before undergoing the test. If you suspect a hepatitis A infection and haven’t been tested for other STDs like chlamydia, syphilis, gonorrhea, HIV, hepatitis B and C, and herpes, our healthcare professionals recommend the comprehensive 10 Panel STD Test to ensure you’re free from all STDs. Many STDs may remain asymptomatic until they cause more severe harm, and having one STD can increase your vulnerability to others.
When to Get Tested for Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious virus that spreads through the exchange of bodily fluids, commonly through sexual contact, shared needles, or intravenous drug use. While the test can detect an HBV infection as early as 3 weeks post-exposure, our clinicians advise testing after 6 weeks for the most precise results. If you are experiencing multiple symptoms or have had close contact with someone with chronic HBV, it is advisable to undergo testing. Including hepatitis B in your routine STD screening is strongly recommended.
Accurate Hepatitis B Testing Process
Our FDA-approved test for hepatitis B virus (HBV) detects the presence of hepatitis B by identifying surface antigens, which are viral proteins. These antigens serve as the earliest indicators of acute infection and are also found in cases of chronic (long-term) infection. Detecting hepatitis B at an early stage is crucial to prevent potential liver health complications. In the event of a positive HBV test result, we conduct a second confirmation test at no extra cost to ensure the highest level of accuracy. Laboratory testing precision is evaluated based on sensitivity and specificity. Our HBV test boasts an 88% sensitivity rate and a remarkable specificity of 99-100%.
Hepatitis B Test Procedure
- Quick 5-Minute Testing Procedure
- Small Blood Sample Required
- Get Results in 1-2 Days
- Phone Consultation with a Doctor for Positive Results
Learn More About Hepatitis B Testing
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that affects the liver and can lead to serious conditions such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. The symptoms of hepatitis B can vary widely from person to person and may include the following: Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes, which is caused by a high level of bilirubin in the blood. Fatigue: Persistent tiredness or exhaustion that doesn’t improve with rest. Pain in the abdomen: Particularly in the area of the liver on the right side beneath the lower ribs. Loss of appetite: This leads to weight loss and malnutrition over time. Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms can be particularly distressing and may lead to dehydration if persistent. Dark urine: The color may appear very dark, similar to tea. Pale stool: Bowel movements might be lighter in color than normal, indicating issues with bile production or flow. Fever: A mild to moderate fever, indicating the body is fighting an infection. Joint pain: Aches and pains in the joints without visible swelling. Weakness and muscle pain: General feelings of weakness or aches in muscles throughout the body.
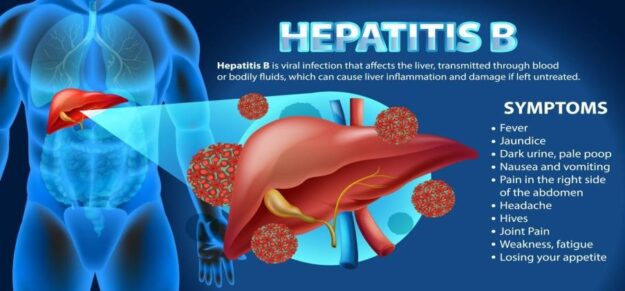
Is Hepatitis B Testing Blood-Based?
Our hepatitis B test requires a blood sample collected by a laboratory technician at the testing center.
Preparation for the Test:
No fasting or special preparation is required. Visit your chosen lab at your earliest convenience.
Who Should Get Tested for Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is often asymptomatic, leading many individuals to be unaware of their infection. Symptoms, when they do occur, may include extreme fatigue, lower abdominal tenderness or pain, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, joint pain, headache, fever, and hives. These symptoms can manifest anywhere from 6 weeks to 6 months after initial exposure to the virus.
What Will the Test Results Show?
The test results will indicate either a positive or negative outcome. A negative result signifies the absence of HBV in your blood sample, while a positive result indicates its presence. If your results are positive, our clinicians are on hand to discuss the findings and address any questions you may have.
Is There a Cure or Treatment for Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B does not have a cure, but in most cases, around 90% of acute infections resolve on their own without long-term concerns. If you test positive for HBV for more than 6 months, it indicates a chronic infection. In such cases, there are treatments available to slow the virus’s progression and protect your liver from damage. Many individuals with chronic HBV can still lead healthy, full lives.
Hepatitis C Antibody Testing Process
Our healthcare professionals employ the FDA-sanctioned hepatitis C Antibody test to screen for hepatitis C. This particular test detects antibodies that the body generates when it detects the presence of the hepatitis C virus in the bloodstream. Our CLIA-certified laboratory technicians collect a small blood sample for the test, eliminating the need for undressing or any uncomfortable swabbing. When evaluating laboratory tests, including STD screening, we consider their accuracy in terms of sensitivity and specificity. Our FDA-approved hepatitis C test boasts a sensitivity rate of 100% and a specificity rate of 99.99%.
Hepatitis C Testing Procedure
Our healthcare professionals employ the FDA-sanctioned hepatitis C Antibody test to screen for hepatitis C. This particular test detects antibodies that the body generates when it detects the presence of the hepatitis C virus in the bloodstream. Our CLIA-certified laboratory technicians collect a small blood sample for the test, eliminating the need for undressing or any uncomfortable swabbing. When evaluating laboratory tests, including STD screening, we consider their accuracy in terms of sensitivity and specificity. Our FDA-approved hepatitis C test boasts a sensitivity rate of 100% and a specificity rate of 99.99%.
Hepatitis C Testing Procedure
- Swift 5-Minute Testing
- Only a Small Blood Sample Required
- Get Your Results in Just 1-2 Days
- Telephone Consultation with a Doctor in Case of Positive Results
Additional Details on Hepatitis C Testing
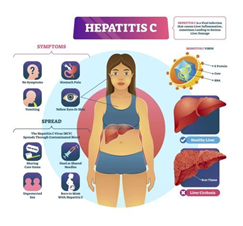
Is Hepatitis C Testing Conducted with Blood or Urine?
Hepatitis C testing involves the Hepatitis C Antibody Test, which is a blood test designed to detect antibodies to the hepatitis C virus in the bloodstream. It requires only a small blood sample for the test.
How Should I Prepare for the Hepatitis C Antibody Test?
No special preparations, such as fasting, are necessary for the Hepatitis C Antibody test since it is a simple blood test.
When Should I Get Tested for Hepatitis C?
Responses to the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) can vary from person to person. Typically, it takes around 8-9 weeks for the body to produce antibodies in response to the virus. Our healthcare professionals recommend testing for hepatitis C after this period. Additionally, it’s advisable to undergo a follow-up test three months after potential exposure to confirm the absence of an active hepatitis C (HCV) infection.
What Will the Test Results Indicate?
- Negative Results: No hepatitis C antibodies were detected in your blood.
- Positive Results: Hepatitis C antibodies were detected in your blood. Note that in rare instances, approximately 10% of positives may be “false positives.” This can occur when past exposure leads to the presence of hepatitis C virus antibodies in your system. If your results are positive, our medical professionals may advise further tests to assess if an active infection is present.
Can Hepatitis C Be Cured or Treated?
Treatment for hepatitis C varies based on whether it’s acute (new) or chronic (persistent). In some cases, no treatment may be required. Hepatitis C often presents with mild flu-like symptoms, and many individuals might not even realize they’re infected. Managing acute hepatitis C involves maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and getting adequate rest. Consultation with a liver specialist is advisable to assess your liver’s health. On the other hand, untreated or chronic hepatitis C can lead to severe liver conditions, including liver failure. Detecting hepatitis C in its early stages enhances the likelihood of treating the infection with fewer complications.
Who Should Consider Hepatitis C Testing?
It is recommended to consider hepatitis C testing if you meet any of the following criteria:
- If you were born between 1945 and 1965 or underwent a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992.
- If you are a current or former injection drug user.
- If you’ve had recent unprotected sexual contact.
- If you reside with an individual who has Hepatitis C. Taking a hepatitis C test as part of your routine STD testing is advisable in these situations.
When Should You Test for Hepatitis C?
Now is the ideal moment to undergo hepatitis C testing and take control of your sexual health. If you’ve engaged in recent unprotected sexual activity with a partner of unknown hepatitis C status or had potential exposure to needles or sharp objects, it’s important to get tested promptly. Timely testing is crucial in preventing acute hepatitis C from progressing to a chronic stage. Typically, it takes around 8-9 weeks for the body to develop antibodies, which is the recommended timeframe for hepatitis C testing.
If you haven’t had recent screenings for other STDs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, HIV-1, HIV-2, hepatitis A and B, herpes-1, or herpes-2 within the past year, our healthcare professionals recommend the comprehensive 10 Test Panel to ensure your complete STD status. We also offer a chlamydia-gonorrhea test panel, as these two infections often coexist, meaning that having one may increase the risk of having the other.
Our Genital Herpes (HSV-2) Testing Process
Discover how we conduct a Genital Herpes (HSV-2) test without the need for uncomfortable swabbing or undressing. We employ an FDA-cleared type-specific genital herpes test that identifies antibodies to distinguish between HSV-1 (oral herpes) and HSV-2 (genital herpes). This test utilizes a simple blood sample. When it comes to laboratory testing, especially for STDs, accuracy is assessed using sensitivity and specificity measures. Our FDA-cleared herpes type 2 test boasts a sensitivity rate of 97% and a specificity rate of 98%.
Herpes Type 2 Testing: Quick and Easy
- Fast 5-Minute Testing
- Only a Small Blood Sample Required
- Get Results within 1-2 Days
Testing for Genital Herpes (HSV-2)
Blood or Urine Test for Genital Herpes?
Our Genital Herpes test employs a blood test known as the Chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) test to detect herpes antibodies.
Test Preparation for HSV-2
No fasting or special preparation is required for the HSV-2 test.
When to Get Tested for Genital Herpes
There’s no one-size-fits-all time to test for genital herpes, as antibody development varies among individuals. While it’s possible to detect herpes-2 as early as 3 weeks after exposure, we recommend waiting 4-6 weeks post-exposure for more reliable results. If your initial test is negative, consider retesting after three months to confirm the results.
Understanding Your Test Results
- Negative Result: No evidence of genital herpes.
- Positive Result: Presence of genital herpes.
- Reliability: While CLIA tests are generally dependable, “false positives” can occur, particularly in populations with low HSV-2 virus prevalence.
- Numeric Range: Test results for herpes are presented as values. A result of 0.91 or lower indicates a negative status, while a result of 1.09 or higher is considered positive.
Is Genital Herpes Curable or Treatable?
Genital herpes is not curable but can be effectively managed. Modern antiviral medications can help prevent symptoms, shorten outbreak duration, and lower the risk of transmitting the virus.
Who Should Get Tested for Genital Herpes?
As per CDC guidelines, HSV-2 infection is more prevalent among women due to easier transmission from men to women. Women who have had recent contact with an individual infected with genital herpes (HSV-2) should consider testing. Infections can be transmitted through contact with genital or oral secretions, lesions, and mucosal surfaces.
When to Get Tested for Genital Herpes
The best time for a genital herpes test is now to ensure your sexual health. Genital herpes often presents mild or easily overlooked symptoms, sometimes mistaken for other skin conditions. For the most accurate results, it’s advised to wait 4-6 weeks after potential exposure before testing for genital herpes. A follow-up test 3 months after exposure is recommended for result confirmation.
While rare, genital herpes can lead to severe complications such as blindness, brain inflammation, and aseptic meningitis. If you’ve recently been in contact with someone of unknown STD status, it’s crucial to get tested promptly.
Moreover, if you haven’t undergone testing for other STDs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, HIV-1, HIV-2, hepatitis A, B, C, or herpes-1 within the past year, our clinicians recommend the comprehensive STD 10-Test Panel to ensure complete STD status verification. We also offer a chlamydia-gonorrhea test panel, as these infections are often found together, meaning having one may increase the risk of the other.
Testing for Oral Herpes (Herpes-1)
Our healthcare professionals employ a type-specific Chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) to detect the specific antibodies combatting the herpes-1 virus in your bloodstream. The skilled technicians in our CLIA-certified laboratories collect a small blood sample for this examination, eliminating the need for disrobing or uncomfortable swabbing. The accuracy of all laboratory tests, including STD assessments, is assessed in terms of sensitivity and specificity. Our FDA-approved herpes type 1 test demonstrates a sensitivity of 96% and a specificity of 97%.
Herpes I Test Procedure
- Quick 5-Minute Testing
- Minimal Blood Sample Needed
- Results Available Within 1-2 Days
Additional Details on Testing for Oral Herpes
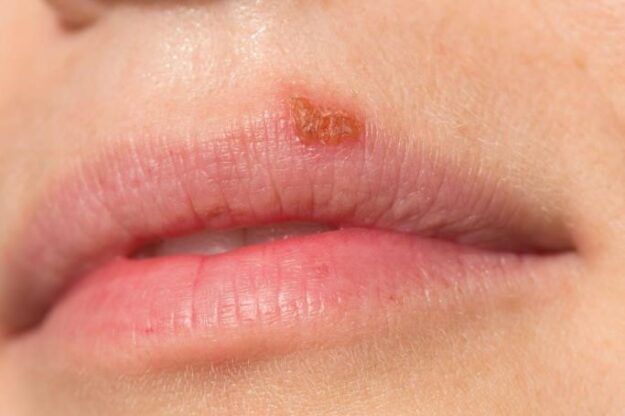
Is the Oral Herpes Test Blood-Based or Urine-Based?
Our oral herpes test is conducted using a blood sample, eliminating the need for undressing or uncomfortable swabbing.
Preparation for the Test
No advance preparation or fasting is required for oral herpes (herpes-1) testing.
Timing for Oral Herpes Testing
Our healthcare experts suggest conducting an oral herpes test approximately 4-6 weeks following initial exposure. It’s essential to include oral herpes testing in your regular STD screening if you’ve engaged in unprotected oral intercourse or have been in contact with HSV-1-infected bodily fluids like saliva or semen.
Interpreting Test Results
A negative result indicates the absence of oral herpes in your system, while a positive result confirms the presence of oral herpes.
Managing Oral Herpes
Oral herpes (herpes-1) cannot be cured, but its symptoms can be managed using antiviral medications. While these drugs do not eliminate the virus from the body, they effectively control outbreaks and reduce the risk of transmitting oral herpes to your partner.
Who Should Consider Oral Herpes Testing?
Oral herpes is a prevalent STD, and individuals who have engaged in unprotected oral sex or have been exposed to infected bodily fluids should consider testing. Given that Herpes-1 symptoms may not always manifest, it’s crucial to undergo testing even if you do not exhibit visible signs of potential infection.
Optimal Timing for Oral Herpes (Herpes-1) Testing
The best time to get tested for Oral Herpes is today. Discover your current STD status now. If you’ve recently engaged in oral sex with a partner whose STD status is uncertain, it’s crucial to undergo oral herpes testing. Our healthcare experts recommend testing 4-6 weeks after potential exposure for the most accurate results. If you suspect exposure, consider re-testing after 3 months, particularly if your previous result was negative. Additionally, if you haven’t been screened for other STDs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, HIV-1, HIV-2, hepatitis A, B, C, or herpes-2 within the past year, our clinicians suggest opting for the comprehensive 10-Test Panel to ensure your complete STD status. We also provide a chlamydia-gonorrhea test panel, as these infections often co-occur, with one infection increasing the risk of the other.
Early Detection HIV RNA Test
Our Medical Experts Recommend the HIV RNA Early Detection Test for Recent HIV Exposure
If you suspect recent exposure to the HIV virus, our medical professionals suggest the HIV RNA Early Detection Test, exclusively available at STDcheck.com. This test is the sole FDA-approved HIV RNA Test currently available. It focuses on the genetic material of HIV, which is RNA, as opposed to antibodies or antigens, enabling earlier detection in as little as 9-11 days post-exposure. Our RNA-based test is the most accurate HIV test in today’s market.
Getting tested for HIV is a straightforward process. Just provide a small blood sample at a nearby lab, and you can be on your way within minutes. With over 4,500 conveniently located testing centers nationwide, there’s likely one near you. Opt for this specialized test to determine your HIV status with confidence.
Typically, HIV RNA test results are accessible within 2-4 business days. Like all laboratory tests, including STD tests, accuracy is assessed in terms of sensitivity and specificity. Our FDA-approved HIV RNA Early Detection test boasts a sensitivity rate of 100% and a specificity of 99.83%.
HIV RNA Test Procedure
- Quick 5-Minute Testing
- Process Only a Small Blood Sample
- Required Results Typically Available in 2-4 Days
- Phone Consultation with a Doctor in Case of Positive Results
HIV RNA Test

Sample Type for HIV RNA Test: Blood
The HIV RNA Early Detection Test is conducted using a blood sample. Our lab technicians will draw a small blood sample for the test.
Test Preparation Requirements
No fasting or special preparation is required.
When Should You Take the HIV RNA Early Detection Test?
The HIV RNA Early Detection Test can provide conclusive results as early as 9-11 days after potential exposure. We are the exclusive online STD testing service offering the FDA-approved HIV RNA Early Detection test.
This test searches for the presence of HIV RNA in patients’ plasma. It can identify acute (new) HIV infections even when antibodies (proteins generated by the body to combat the HIV virus) are not yet present in the bloodstream. This makes the HIV RNA test the most sensitive and precise HIV RNA Early Detection test currently accessible.
Understanding Test Result Interpretation
- Negative Result: No HIV was detected.
- Positive Result: HIV was found in your bloodstream.
- In the event of a positive result, a confirmation test will be conducted on the same blood sample at no extra charge to validate the outcome.
It’s important to note that a positive result for the HIV virus does not indicate that you have AIDS.
HIV RNA PCR Test
PCR, which stands for polymerase chain reaction, is a method used to detect the presence of HIV genetic material (RNA) in a sample. This test examines a blood sample for early infections, even before the body has generated antibodies.
HIV RNA Test Window Period
HIV RNA tests are employed to identify the presence of the HIV virus in the collected sample. There is a very brief window, typically around 9 days post-infection, to detect the virus using this test. Although it is not commonly used for general screening due to its higher cost, it offers only a slight advantage over antigen/antibody tests, which are more budget-friendly. Nevertheless, HIV RNA tests are often conducted as a follow-up to confirm a positive HIV test result. They can also be used for specific situations, such as when an individual has recently been exposed to HIV and is exhibiting symptoms of early HIV infection.
HIV RNA Test Window Period CDC The CDC
advises that an RNA test can identify early HIV infection if taken within 9 to 11 days after potential exposure. This window period is recommended for RNA testing because standard antibody tests may not yet detect the presence of HIV, according to the CDC.
When to Consider the HIV RNA Early Detection Test
As per CDC reports, approximately 1.2 million individuals in the United States were living with HIV by the end of 2012, the most recent year for which data is available. Of these, around 13%, or 1 in 8, were unaware of their infection. The U.S. sees nearly 50,000 new HIV infections diagnosed each year. Given these alarming statistics, undergoing an HIV RNA Early Detection test is essential.
If you’ve recently engaged in unprotected sexual activity, you may have been exposed to the risk of HIV and other STDs. Our 10-Test Panel covers major STDs, including HIV Types 1 & 2. Our medical professionals advise taking the HIV RNA Early Detection Test within 9-11 days after potential HIV exposure.
HIV RNA Test Accuracy at 11 Days
The HIV RNA test is approximately 95 to 99% accurate when taken within 9-11 days after potential exposure.
When is the HIV RNA Test Considered Conclusive?
The HIV RNA test is considered approximately 99% conclusive around 28 days after potential exposure. However, its accuracy decreases three months after exposure. This decline in accuracy is attributed to the body’s production of antibodies to combat the HIV virus. Consequently, the detectable amount of the virus in the blood may decrease below the RNA test detection limit.
Confirmation of HIV Testing Results
HIV testing is generally highly accurate, but false positives can occur. These tests assess the presence of HIV antibodies in the sample, which are proteins generated by the immune system in response to foreign substances, such as HIV. False positive results often happen when the test detects antibodies that are not related to HIV but might be produced in response to another virus or infection. While these tests are designed to specifically detect HIV antibodies, errors can occasionally occur.
Several factors can contribute to false positives, including the subjectivity of the testing device, borderline results that may require interpretation by an experienced staff member, sample mishandling or mix-up with another patient’s, and clerical errors. In some cases, individuals who have received a flu vaccine or are part of an HIV vaccine study may receive a false positive result.
This emphasizes the importance of choosing a reputable and trusted provider with a history of accurate results. Our laboratories have a longstanding track record of precision and have been serving patients for many decades. Our highly trained medical staff is dedicated to meeting your needs with care and accuracy.
How We Perform Syphilis Testing
Our medical professionals utilize the Rapid Plasma Reagin (RPR) syphilis test, which identifies antibodies produced in response to a syphilis infection. In the case of a positive result, a Treponema Pallidum Assay (TPA) test is employed to confirm the presence of the syphilis-causing bacteria.
Testing for syphilis is crucial because you can have an asymptomatic infection and unknowingly transmit it to your partner. Like all laboratory testing, including STD tests, accuracy is assessed in terms of sensitivity and specificity. Our FDA-cleared syphilis test demonstrates a sensitivity rate of 95% and a specificity of 91%
Syphilis Test Procedure
- Quick 5-Minute Testing
- Process Small Blood Sample Required
- Results Typically Available in 1-2 Days
- Phone Consultation with a Doctor in Case of Positive Results
Learn More About Syphilis Testing
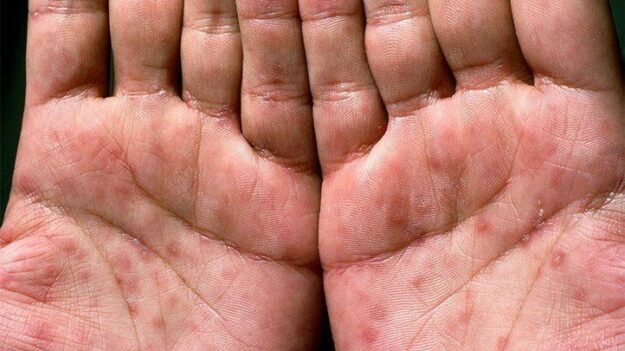
Sample Type for Syphilis Testing:
Blood A small blood sample is used for syphilis testing.
Test Preparation Requirements
No preparation or fasting is required for the syphilis test.
When to Consider Syphilis Testing
For the most accurate results, it’s recommended to wait a minimum of 3-6 weeks after potential exposure before getting tested for syphilis. If you’ve received treatment for syphilis, it’s crucial to undergo a follow-up test 3 months later to ensure the complete clearance of the syphilis infection.
Understanding Syphilis Test Results
Syphilis test results can yield two potential outcomes: positive (reactive) or negative (non-reactive). A negative result indicates the absence of detectable syphilis traces in your system. A positive result suggests the possibility of a syphilis infection. However, a definitive diagnosis of syphilis can only be confirmed after a TPA confirmation test, which distinguishes syphilis from other conditions, is conducted.
Is Syphilis Curable or Treatable?
Yes, syphilis is a curable infection that can be effectively treated with antibiotics. If you receive a positive syphilis test result, our medical professionals are ready to provide a phone consultation at no extra charge to discuss your results.
Who Should Consider Syphilis Testing?
If you are sexually active, you are susceptible to syphilis infection. Syphilis is not only easily transmissible but can also remain dormant for many years without any noticeable symptoms. The most reliable way to ascertain your syphilis status is through testing. Regular syphilis testing is recommended as a vital component of your routine STD screening, particularly if you have engaged in unprotected sexual activity and are uncertain about your partner’s status.
When to Get Tested for Syphilis
The ideal time to undergo a syphilis test is now. Determine your sexual health status today. If you’ve had recent contact with someone whose STD status is unknown, testing is crucial.
Our medical experts advise syphilis testing at least 3-6 weeks following potential exposure, with a follow-up test after three months to confirm clearance of the syphilis infection. Additionally, if you haven’t been tested for other STDs, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, HIV-1, HIV-2, hepatitis A, B, C, herpes-1, or herpes-2, within the past year, our clinicians recommend the comprehensive 10 Test Panel to ensure you are completely free from STDs. We also offer a chlamydia-gonorrhea test panel, as these infections are often found together, with one infection increasing the risk of the other.